This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Pacific EMIS Systems Administrator Guide
Introduction
For an introduction to this project refer to the Pacific EMIS User Guide and Developer Guide both offering a detailed background for their respective target users. Otherwise, this is a systems administrator guide and it is understood that the person filling this role is familiar with the project. This guide instead focuses on aspects such as deployment into production and maintenance which includes upgrades, backups and how to report problems so they get fixed. A clear release history with versioning done following the Semantic Versioning Standard will also be included.
New Deployment
A new deployment is done when a new country adopts the Pacific EMIS. Currently a new deployment requires a few tedious steps which only need to be done once and future upgrades are much easier.
Operating System
Currently only the Windows operating system is supported. The application can be installed on any recent version of the Windows operating system.
| Operating System | Version Number |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 | 10.0* |
| Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview | 10.0* |
| Windows 8.1 | 6.3* |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 6.3* |
| Windows 8 | 6.2 |
| Windows Server 2012 | 6.2 |
| Windows 7 | 6.1 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 6.1 |
| Windows Server 2008 | 6.0 |
If this is a first time trying this out it is recommended to try on a test virtual machine. VirtualBox is a free virtualisation technology great for trying this on your personal machine. If you are new to virtualisation their documentation is good, if you have used other virtualisation platforms already you can actually download and start using it right away, it is that easy.
Install .NET 4.6 Framework
Install .NET 4.6 Framework by downloading the web installer and running it, of course a good Internet connection will be required.
Create Account to Run the Application
Create a Windows user account (on local machine or active directory) to run the application. Call this new user something like EMISWEB for a deployment in Marshall Islands. This new user should both be owner of the SQL database and the one running the IIS web process.
Active Directory Server
The Pacific EMIS typically needs an Active Directory to manage users, groups and roles (i.e. access permission levels). You might find yourself in one of the following scenarios:
- Your organisation already runs an Active Directory in which case this is great, things will be much easier
- Your organisation do not run an Active Directory in which case you will need to deploy one and join workstations to the domain. You have the choice of Microsoft Server's Active Directory or the free open source Samba4
- Your organisation does not run an Active Directory and uses Google Accounts in which case you can will need to deploy a local Active Directory and use Google Sync to sync users between both system
Database Engine Installation
The only database engine currently supported is Microsoft SQL Server (MSSQL Server) with most deployments only tested with MSSQL Server 2012 or MSSQL Server 2012 Express Edition. There is no need for an expensive license and the Express edition which is freely available will work fine for this application. If you don't have already a commercial license download the free version MS SQL Server Express. Any of the files would have the required minimal database engine but might has well download the 64bit full version called ENU\x64\SQLEXPRADV_x64_ENU.exe. Double click and follow through the installation. Choosing the default values is a good start and reboot the system when done.
Restoring the Main Application Database
There are two main ways to installed the main application database:
- Restore the application database (e.g. FEDEMIS, MIEMIS, SIEMIS, etc.) from a backup given to you by one of the experienced developers (geared towards systems administrators)
- Restore the schema from the hosted service and fill up core and meta data yourself (geared towards developers)
The first option should be your choice unless you are an experienced developer of the EMIS system. If that is the case you can restore from the latest schema by connecting to a hosted service with the local Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) though currently you must be given access to achieve this.
Open SSMS and connect to the hosted service to get the empty current database as shown on the following screenshot.

You may have to increase the Connection time-out in Options and this will require a reliable Internet connection. The database engine connection details are:
- Server: VCNSQL90.webhost4life.com,1433
- Authentication: SQL Server Authentication
- User: youruser
- Password: yourpassword
When you successfully connect to the hosted server you should see a database called pineapples which is the empty database to start with.
Backup this database locally and then restore it into your local database engine with a new name (e.g. MIEMIS for Marshall Islands, SIEMIS for Solomon Islands). This will now serve as your starting point. The only data in this “reference” database is data that is unequivocally “system-defined” and will of necessity be the same in every implementation no matter what country (e.g. metaNumbers,) so a new system can safely begin by backing up and restoring this database.
If backup and restore of databases with MSSQL Server is new you to you refer to backup and restore as starting point.
Main Configuration
Most of the configuration resides in the database and most must be loaded there manually. In this project, most of this configuration is called lookups and meta data and are described in the spreadsheet available here (
Once all the required data has been localised (only the features necessary need to be done, other should be safely ignored) the necessary SQL command to load the data into the database must be prepare. How to automate this work depends on the preference of the responsible person, some developers prefer to use an Excel function to generate the SQL others prefer to manipulate this into their text editor of choice. Whatever the preferred approach you should end up with a file containing all the SQL to load the data which would look like this (
Setting Up the IdentitiesP Database
The Pacific EMIS makes use of another auxiliary database called IdentitiesP where two main things are managed: the concept of ASP.NET user, roles and claims, and some details about the navigation system. When deploying a new DB you'll need that one to be given to you by one of the team members.
Restore this database backup into a database called IdentitiesP. There is a little work to do in this database. For example, it can be used to control the menu showing in the web UI. For example, if a country is not quite ready to adopt a specific feature or simply does not need need it can essentially be deactivated from the deployment by doing a simple modification to the data in table Navigation from the IdentitiesP database.
More details about how this works is documented in the Developer Guide in High Level Architecture in Navigation and Module System. But from a systems administrator's point of view you can simply move on to the next section to configure the modules for your country.
Module Configuration
Modules in the Pacific EMIS are essential features (e.g. Performance Assessments, Schools, Teachers). Not all Pacific countries will require (or even be ready) for all feature of the system. Eventually it would be nice to be able to login as Administrator and check mark desired modules directly from the UI, but until then, you can in effect enable and disable modules by taking them out of the menu. The table Navigation in IdentitiesP defines the hierarchy shown in the side bar menu.
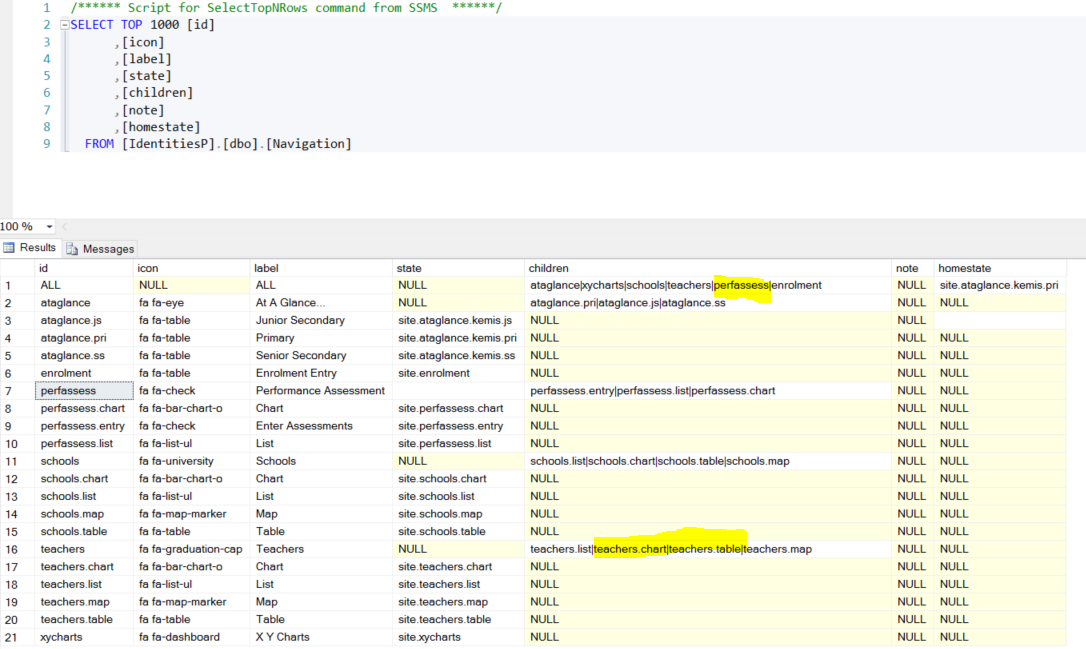
So for example, you can remove perf assessments by removing it from the children of ALL. I would expect the structure of this to be different from site to site. The leaf nodes define the icon text, and ui-router state associated to the task. For users defined using ASP.NET identity logins, the menu they are given is defined by the MenuKey on AspNetUsers. If you log in using a domain login, you currently get menu key ALL, as previously mentioned, the missing piece here is some mapping between domain groups and user profile to determine the menu key, Roles and filters.
Make User Owner of both Databases
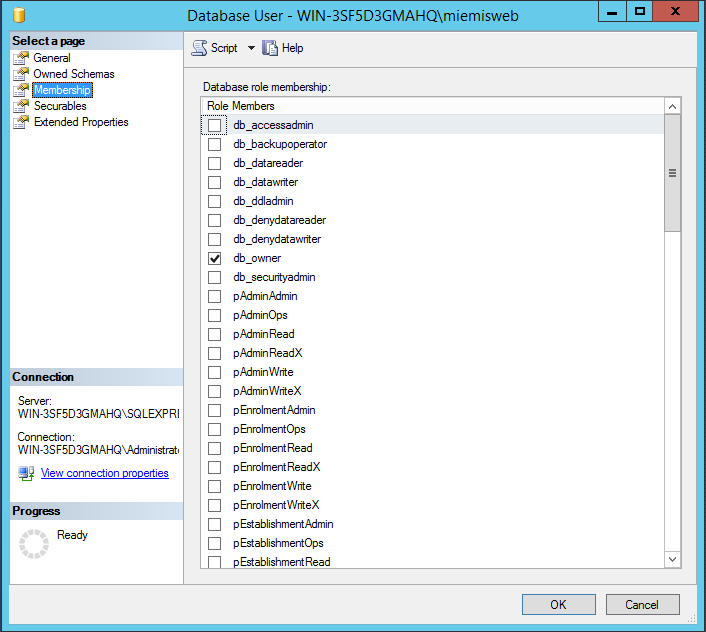
Add this user as db_owner of the database created earlier in Setting up the New Empty Database. You can do this by opening SSMS, browsing to the new database created early on then click Security–Users where you can add a new user as show in the following figure (select Windows user from User Type). Locate the Windows account miemisweb and create it.
Next assign the db_owner to that new user in Membership as shown below.
Do the same as above for the IdentitiesP database.
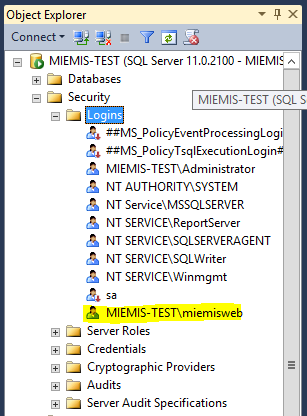
Give User Login Permission
The user created in Create Account to Run the Application must be given permission to login the SQL Server. Do this in the MS SQL Management Studio by adding the user as shown below.
Deploy the Application
Deployment Method
The application is deployed using a dropbox share. If you do not have an account create one on the Dropbox website and install their dropbox PC application. Your account and the dropbox application should be accessible from both the development machine and the production machine where the Pacific EMIS is to be deployed. And your account should be given access to a share called WebInstall by one of the Pacific EMIS maintainers. Using your own dropbox account for this is fine to get started and test deployment (e.g. training purposes, practice on your own machine) but the actual real production deployment should be using one of the organisation's dropbox account, one perpetually accessible by the current technical responsible person of the organisation (e.g. admin, sysadmin, system are common accounts for this).
Deployment Configuration
The share WebInstall contains a folder called Pineapples which has the application. The Pacific EMIS software project maintainer is usually the one preparing this folder with the latest releases. Before moving to the next step this is a good time to create a folder to hold some key files for your country of deployment. For example, in RMI the folder RMI-deployment-files was created in the WebInstall share. This folder can hold among, other things, the logo (rename it miemis.png,) the lookups spreadsheet and the SQL script generated from the spreadsheet.
Next you must edit the deployment configuration file called Web.config. You can find it in the dropbox WebInstall (e.g. C:\Users\Administrator\Dropbox\wwwroot\WebInstall\Pineapples\Web.config). Then open it and edit the following three section to configuration the databases access. The example below is for Marshall Islands: it uses miemis-test for database name, miemis for context and the SERVERNAME\SQLINSTANCENAME will depend on the server it is being deployed on.
<connectionStrings> <!-- Connection to the Identities database , note the factory seetting below will generate this database if going "code first" this connectin string is referenced in ApplicationDbContext constructor --> <add name="DefaultConnection" connectionString="Data Source=SERVERNAME\SQLINSTANCENAME;Initial Catalog=IdentitiesP;Integrated Security=True" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" /> </connectionStrings> <!-- For a description of web.config changes see http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=235367. The following attributes can be set on the <httpRuntime> tag. <system.Web> <httpRuntime targetFramework="4.5.1" /> </system.Web> --> <appSettings> <add key="server" value="SERVERNAME\SQLINSTANCENAME" /> <add key="database" value="miemis-test" /> <add key="context" value="miemis" /> <add key="title" value="MIEMIS Online" /> <add key="ReportServerUrl" value="http://localhost:8080/reportserver" /> <add key="FileDb" value="d:\files\filedb"/> </appSettings>
<parameter value="Data Source=SERVERNAME\SQLINSTANCENAME;Initial Catalog=IdentitiesP; Integrated Security=True; MultipleActiveResultSets=True" />
Deployment Copy to IIS inetpub
Now use the deploy.bat script to copy files into the IIS folder (i.e. C:\inetpub\wwwroot\). You'll have to do it through the command line. From the Windows menu open the command prompt then change directory to the dropbox share and then run the script (ignore the warning at the end and press enter when presented with pause), should be something like this:
> cd C:\Users\Administrator\Dropbox\WebInstall\Pineapples\ > deploy.bat miemis
This will create the folder C:\inetpub\wwwroot\miemis with most of the necessary application. Now will be put in the remaining missing files: the Web.config, miemis.png logo and the Global.asax files. If you have already put your logo into C:\Users\Administrator\Dropbox\WebInstall\RMI-deployment-files as instructed earlier then the following commands should copy the files in the right place (you could do it from the Windows Desktop too)
> mkdir C:\inetpub\wwwroot\miemis\assets_local > copy C:\Users\Administrator\Dropbox\WebInstall\Pineapples\Web.config C:\inetpub\wwwroot\miemis\ > copy C:\Users\Administrator\Dropbox\WebInstall\RMI-deployment-files\miemis.png C:\inetpub\wwwroot\miemis\assets_local > copy C:\Users\Administrator\Dropbox\WebInstall\Pineapples\Global.asax C:\inetpub\wwwroot\miemis\
Web Server (IIS)
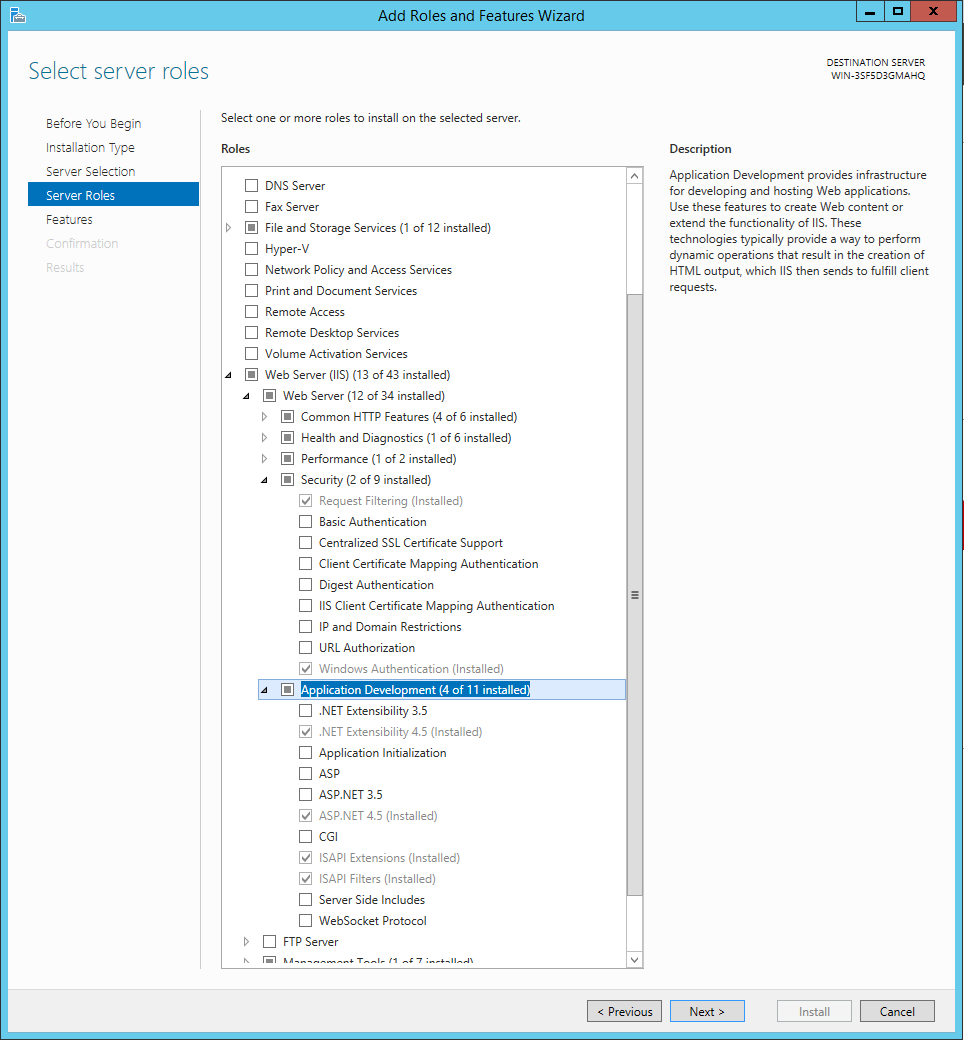
Enable the IIS Role
To enable to Web Server (IIS) on the Windows Server open the Server Manager and find Add Roles and Features. Find the Web Server (IIS), enable it and make sure it contains the following minimum functionalities.
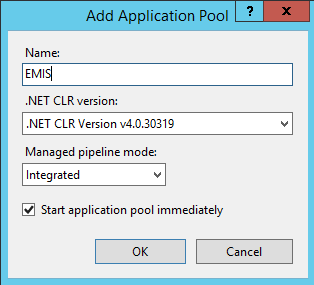
Create an Application Pool
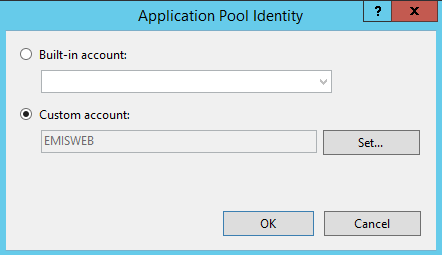
Next open the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager and right click on Application Pools and Add Application Pool.. to create an application pool called EMIS as shown in figure below. An application pool is essentially an isolated server worker process running that will run our application.
Apart from the default setting as shown in the above figure you will need to go in the new EMIS application pool's Advanced Settings… and configure the Identity to the Windows account EMISWEB we created earlier. Select the EMIS application pool and Advanced Settings…. The steps involved in setting the custom identity are depicted in the following figure.

Choose custom account and enter the details for your newly created local account;
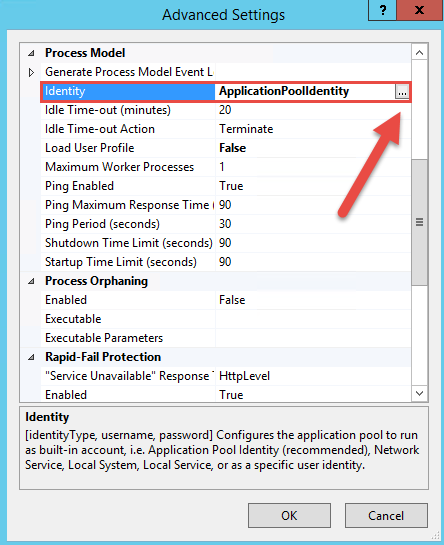
Choose custom account and enter the details for your newly created local account;
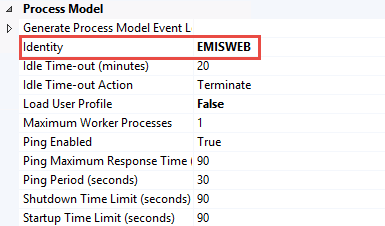
Next on the EMIS app, choose manage app and advanced settings;

And change to run in your newly created Application Pool

You may have to Stop and Start the application pool for this to take effect. Next, look for your new website in Sites–Default Web Site, in this case it is miemis. Right click it and Convert to Application, something that will look like the following.

Once this is done you can test by point your browser to http://server-name/miemis.
Exams Data Integration
NMCT XML Data File Transfer Format for Micronesia
The xml file prepared for importing into FedEMIS contains all the necessary information to generate the graphical reports. It includes the text of achievement levels, benchmarks and standards to provide maximum referential independence. Schools are only referenced by their school_ID as stored in FedEMIS. Facility for a Student_ID is attached to every student, however this is currently blank.
The top level XML structure is as follows;
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no" ?> <NMCT> <NMCT_test> ............... Information about the test </NMCT_test> <Curriculum> ............... Standards, Benchmarks and Achievement Levels used in this test </Curriculum> <Students> ............... Student information including name, state, school and gender. <Results> ............. Student achievement levels for each benchmark assessed in the test. </Results> </Students> </NMCT>
In more Detail
<NMCT_test test_group_ID="R06"> <Test_name>Year 6 Reading</Test_name> <Year>2016-17</Year> </NMCT_test>
Attribute: test_group_ID places this test into a group of tests. A display option requires that data from three consecutive tests be displayed concurrently. This information enables this test to be located in a set of like tests when combined with <Year>
<Curriculum> <Standards> <Standard Standard_ID="ELA.2"> <Standard_description>Reading</Standard_description> </Standard> </Standards> <Benchmarks> <Benchmark Benchmark_ID="ELA.2.6.1" Standard_ID="ELA.2"> <Benchmark_description> Identify and use a variety of word strategies to build meaning </Benchmark_description> </Benchmark> </Benchmarks> <AchievementLevels> <AchievementLevel AchievementLevel_ID="1"> <AchievementLevel_name> Well below competent </AchievementLevel_name> </AchievementLevels> </Curriculum>
This data sets up the standards / benchmark relationship. Whilst the relationship in the FSM case can be interpreted from the coding, this should not be assumed.It also provided the text, internal identification and number of the achievement levels. Whist this information is stable in FSM, it varies between countries in order to make the graphical displays as generic as possible.
<Students> <Student Student_ID=""> <Student_name>Daiamarleen Francisco</Student_name> <Gender>Female</Gender> <State>Chuuk</State> <School School_ID="CHK066"/> <Results> <Result AchievementLevel_ID="4" Benchmark_ID="ELA.2.6.1"/>
Student_ID would be the national student ID if available. Gender is “Male” or “Female” but there are some spelling issues and missing data School_ID is looked up using a NMCT to FedEMIS table. Some NMCT schools in older data sets do not exist in the current EMIS.
PDF eSurvey Technology
An important part of the deployment is the PDF eSurvey Technologies. This is a little different then the remaining of the deployment as it is not part of the web application but seperate components of the whole Pacific EMIS system.
Getting the eSurveys on the Server
First you will need the actual PDF eSurveys. Those are the PDF used to collect data on the field without a good Internet connection. There are several ways you can get the eSurveys on the server. But one convenient way is to create a bitbucket.org account for the organisation (e.g. in RMI we use the Google email admin@pss.edu.mh for these things). This way you can then install SourceTree by the same company. The advantage of getting the eSurveys this way is that is becomes easy to get newer versions of the surveys by pulling them from the central repository where their changes are managed. If you are new to this sort of technology you could start by reading about version control.
Once you create a bitbucket account you can point your browser to the pineapples.esurvey repository and make sure you are logged in. Then you can “clone” the pineapples.esurvey repository by clicking on the button as shown in the following image and open it in SourceTree.
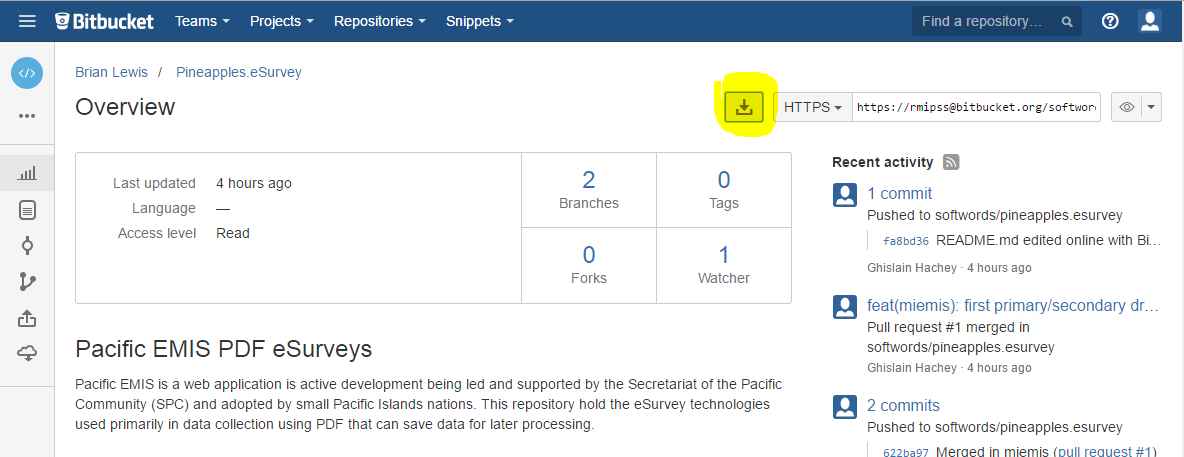
Then when SourceTree opens you will be prompt with the following where it would be a good idea to edit the location as shown below.
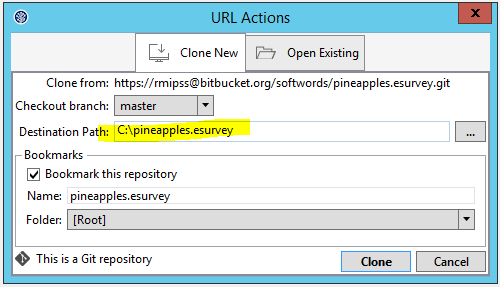
If you followed the steps above all your surveys files should be in C:\pineapples.esurvey\miemis\. You don't really need to keep the SourceTree application open anymore unless you want to pull in latest
survey changes.
PDF eSurvey Technology Manager
Second you need to install the PDF eSurvey Technology Manager. Currently this is a standalone desktop application that must be installed on a machine to “manage” eSurveys, in other words, it aims at doing the following:
- Read existing school surveys from a database (production or a test database)
- Pre-populate surveys with some data before sending them to schools
- Upload completed surveys into the database (again, production or a test database)
The installation should be done one time on the machines of the data entry officers. The first step is to download the PDF eSurvey Manager (
- P:\SIEMIS\eSurveys\intray
- P:\SIEMIS\eSurveys\outtray
- P:\SIEMIS\eSurveys\pre-processing
- P:\SIEMIS\eSurveys\template
Double click to install it, you should see the following screenshot.
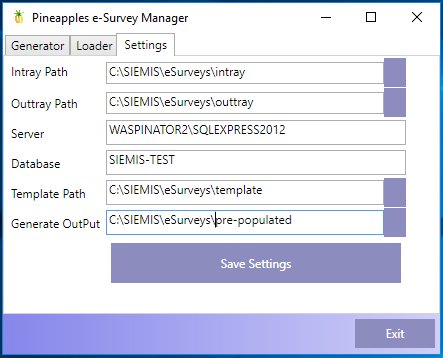
Start with the configuration as explained below.
- Intray Path: is where completed PDF eSurveys should be dumped
- Outtray Path: is where the tool puts the PDF eSurveys once that have been successfully processed and entered in the database
- Server: is the instance name of the SQL Server
- Database: database is the name of the database
- Template Path: should whole an untouched copy of the PDF eSurveys (e.g. Examples)
- Generate OutPut: is where the PDF eSurveys are prepopulated with some data before being sent to schools for completion
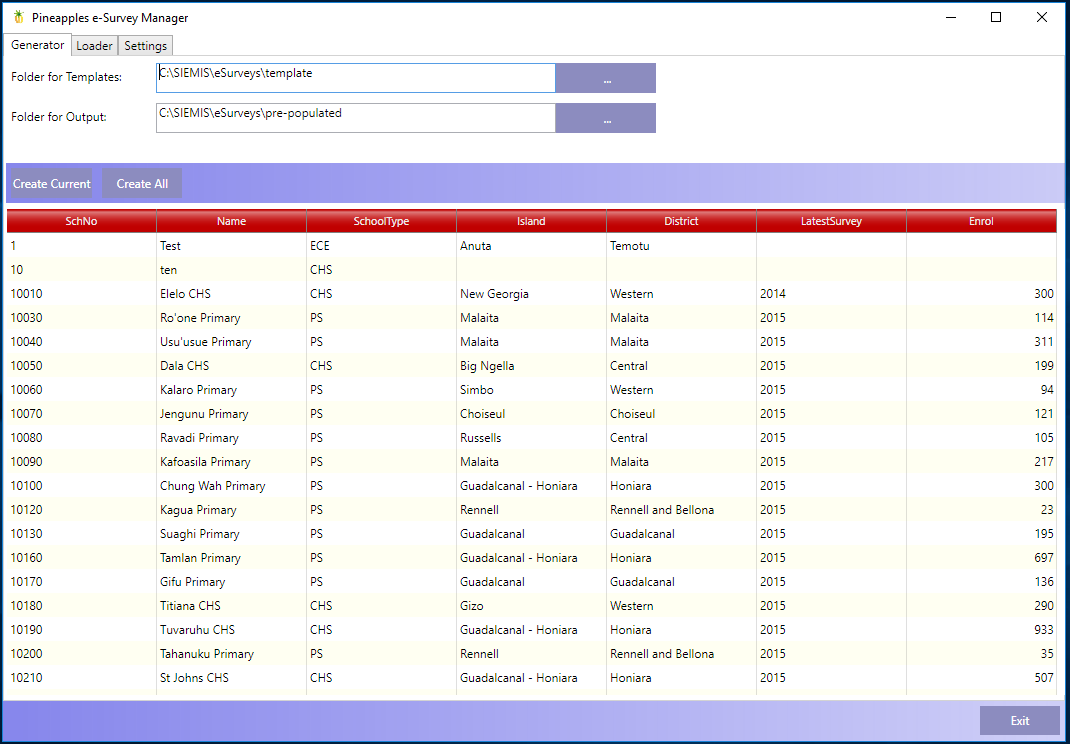
With the settings saved you should see something like the following when starting the tool. This is a list of the current surveys by school already in the database and shows under the Generator tab.
Now is a good time to browse the other tab called Loader. The Settings tab is the same as the one on startup.
How to use this tool is documented in the User Guide.
Upgrade
Currently upgades are done using Dropbox by a developer with write access to the dropbox share. Essentially, a dropbox account runs on the developer's machine and also on the production machine running the EMIS.
Cutting a Release
No official releases are currently being cut. The way upgrades work currently is a developer brings his local develop branch up-to-date with origin/develop branch which contains the most up-to-date application. Note that this process will eventually improve.
Sync Latest to Dropbox
Once the local develop branch is up-to-date. Open the dropbox share which should look like the following image. The script updateFromDev.bat simply copy only the necessary files for deployment into production into the same folder. The extra ones such as the highlighted one updateFromDevToHere_GH.bat is simply a convenience to the developer which likely has a different location for his/her repository. Double clicking that script will sync the local develop branch to the dropbox fairly quickly.
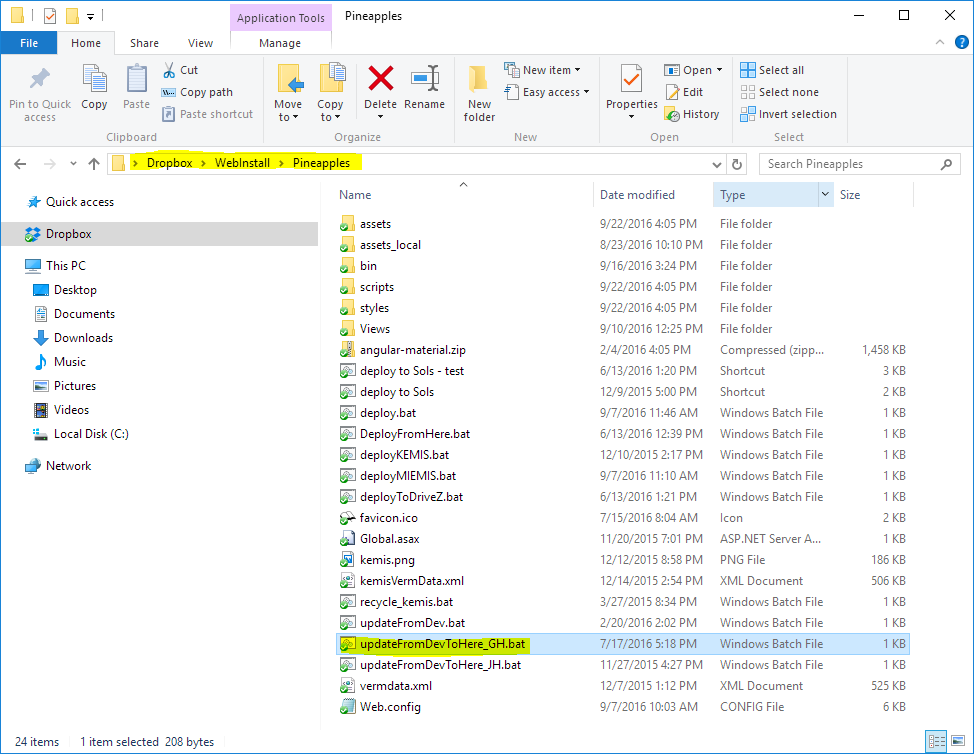
Wait until the dropbox sync is complete
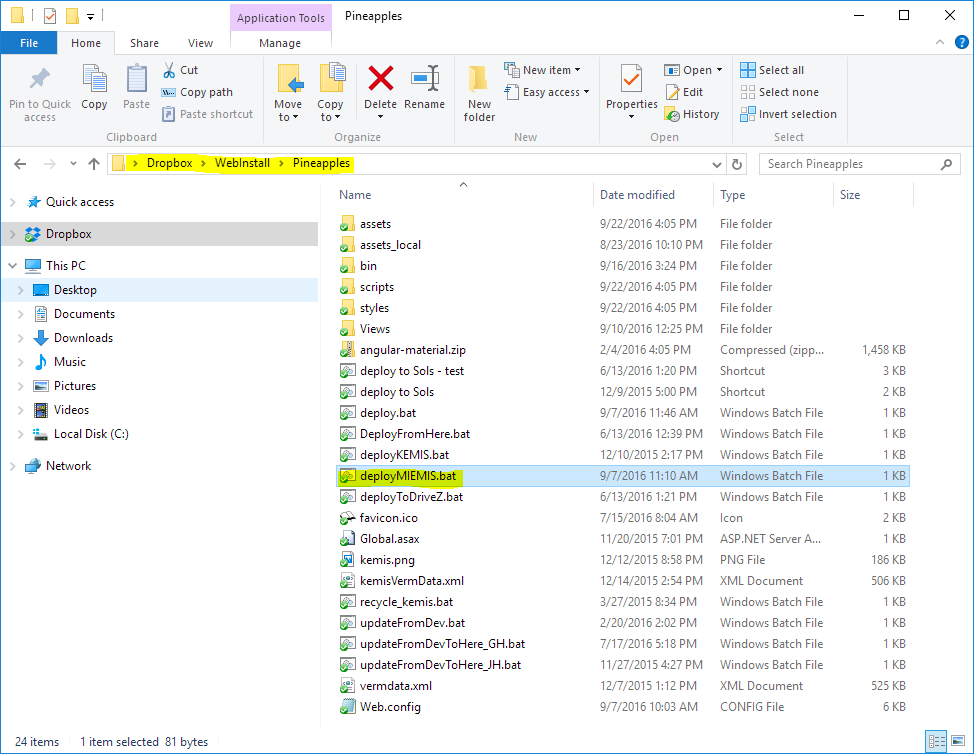
Sync Latest to Production
Login the production server using remote desktop or equivalent. Open the drop box folder as it is shown in the following image. If you have a good Internet connection by the time you get to the production dropbox might have completed the sync, otherwise wait until it is synced also locally on the production server. Then double click on the deployMIEMIS.bat which is a convenient wrapper script to call the deploy script with configuration specific to MIEMIS in Marshall Islands.
Database Schema Change
Most upgrade will not require an upgrade to the DB schema but occasionally some will. In those case it is best to use SQLDelta to look through each change and carefully apply them.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
There are two main was backups are conducted.
- Platform backup which backs up the whole operating system (virtual machine), its configuration, the data and everything in needed for a single click recovery.
- Data backup which only backs up the database using MS SQL Servers database backup feature, and everything in
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\miemisthe folder holding the application
Platform Backup
Nightly backup of the whole production server should be done and a copy stored locally and another stored to a remote location. Backup recovery should be tested twice a year at least to make sure they are working as expected.

Data Backup
Useful to quickly move the whole production system to the MIEMIS-TEST to test MIEMIS upgrades before executing the upgrade into production. Simply backup the DB on MIEMIS-PROD, or whatever your production server is called along with C:\inetpub\wwwroot\miemis and move all of it to MIEMIS-TEST, or whatever your test server is and::
- Restore the DB into an already installed SQL Server
- Deploy the application in IIS (this can also be done by simply sync'ing dropbox if you are already setup for it on the test machine)
Reporting Issues

Release History

